Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic Imaging
As part of our mission to provide the latest innovations in veterinary medicine, CUVS offers advanced imaging modalities. These are essential medical tools, enhancing our diagnostic and treatment capabilities and enabling our specialists to use the most appropriate technology for your pet.
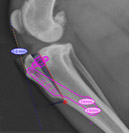
Digital radiography (x-rays)
Digital radiography utilizes digital sensors that yield high resolution images, allowing for better visualization as well as electronic sharing and storage. All radiographs at CUVS are interpreted by board-certified radiologists. Ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to image internal organs and structures. It is considered the modality of choice for many conditions. Ultrasound-guided aspirates and biopsies allow the specialist to obtain diagnostic samples in a minimally-invasive yet controlled manner.
Orthopedic planning
Specialized orthopedic software is used for planning of orthopedic procedures such as cruciate rupture repair, limb deformity, fracture and joint reconstruction. This enables magnification, precise measurement, and “virtual surgery”, improving outcomes.
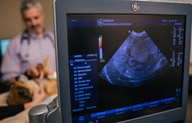
Ultrasonography
Ultrasound uses reflected sound waves to image internal organs and structures. It is considered the modality of choice for many conditions. Ultrasound-guided aspirates and biopsies allow the specialist to obtain diagnostic samples in a minimally-invasive yet controlled manner.
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound of the heart and blood vessels to assess heart function and diagnose cardiac conditions. Sophisticated echocardiography at CUVS enables visualization of the heart muscle and valves as well as evaluation of blood flow patterns (via color flow doppler).
Cavities, to delineate the margins of tumors, to guide surgery or other procedures, to diagnose certain muscle and bone disorders, and to evaluate conditions of the nasal cavity, ear, sinuses, brain or spinal cord. All scans at CUVS are interpreted by board-certified radiologists.
Computed tomography (CT scan)
The CT scan rotates around the body, obtaining multiple images in cross-sectional “slices” (rather than 2-dimentional images produced by routine X-rays). The CT computer then compiles these into 3-D images of the pet’s internal structures, enabling very detailed evaluation of soft tissue, bone and blood vessels. CT scans are used to search for cancer, to better evaluate body cavities, to delineate the margins of tumors, to guide surgery or other procedures, to diagnose certain muscle and bone disorders, and to evaluate conditions of the nasal cavity, ear, sinuses, brain or spinal cord.
CUVS has a 128-slice CT scanner, the most advanced in the region. This means faster and superior quality scans that are safer for the patient and better able to diagnose complex disorders. Advanced technology enables our board-certified radiologists to visualize and manipulate the scan images real-time so that the medical teams can make immediate decisions, and to produce 3-dimensional models that can be displayed in the surgical suites to guide surgery.
Fluoroscopy (C-arm)
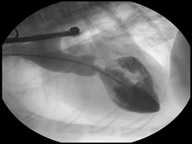
Fluoroscopy is like an ”x-ray movie”; it uses x-ray images to produce a real time, moving 2D image that’s displayed on monitors. In this way, we can see inside the body while the organs are moving, facilitating evaluation of the airway during breathing or the esophagus during swallowing. Sophisticated fluoroscopy, like we have at CUVS, also enables advanced interventional procedures, such as stent placement (trachea, urethra, ureter) or ureteral bypass, pacemaker implantation, and repair of some congenital heart conditions.
Angiography
Angiography is used to visualize blood vessels. Using an intravenous contrast agent and imaging modalities such as fluoroscopy or radiology, we can visualize a pet’s veins, arteries and heart chambers.